
This will display the URL of the repository you created on GitHub. We’ve got a whole bunch of existing articles and screencasts and more to come. You should have already created a GitHub account in the Setting Up Git lesson. You can set it up globally: $ git config -global toSetupRemote trueīranch 'demo' set up to track 'origin/demo'. This is what the toSetupRemote configuration option is for (available since Git 2.38, October 2022).

What if I told you that Git can now automatically manage the remote branch creation and tracking with a simple git push? This is quite constraining, especially since 99% of the time we only have a single remote repository and use same-name branches.
It also tells Git to setup a (default) tracking between your local branch and the remote branch you’re pushing to (then you’ll be able to use the shorter git pull and git push later on, without specifying the remote repo or branch). git fetch can fetch from either a single named repository or URL, or from several repositories at once ifwhat remote repository (yes, you can have multiple remote repos),.The git push command has only -u aka -set-upstream, which takes no argument. Upstream, see 'toSetupRemote' in 'git help config'. The git branch command has both -set-upstream and -set-upstream-to, with the former deprecated in favor of the latter for the reason already given in Nick's answer. To have this happen automatically for branches without a tracking To push the current branch and set the remote as upstream, use

Run the git push -set-upstream origin command. $ git pushįatal: The current branch demo has no upstream branch. If the remote is fetched successfully, add upstream (tracking) reference, used by argument-less git-pull1 and other commands. To set upstream the local branch, firstly, move to the Git repository and clone remote repository. Instead, it prints a message that suggests to explicitly type the following command: git push -set-upstream origin.
If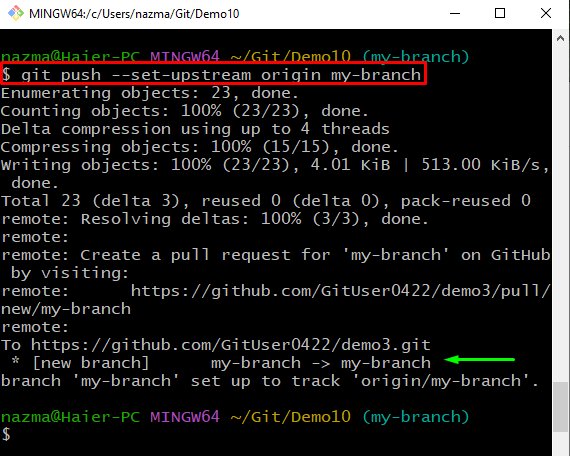
org :my-user/some-project. That setting can be overridden by using the -track and -no-track options, and changed later using git branch -set-upstream-to. org :my-user/some-project.git (fetch) origin git bitbucket. If you’re a command line user, you probably noticed that Git does nothing on the very first push of a branch. First, verify that you have already setup a remote for the upstream repository, and hopefully an origin too: git remote -v origin git bitbucket.
#GIT SET UPSTREAM URL CODE#
If you open a folder that is a Git repository and begin making changes, VS Code will add useful annotations to the gutter and to the overview ruler. This will let you publish the current branch to a remote. Cette page est également disponible en français. If there is no upstream branch configured and the Git repository has remotes set up, the Publish action is enabled.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
